What is CNC milling
CNC is an acronym for ‘Computer Numerically Controlled’. In manufacturing what is controlled is tool movement, whether it is an extrusion nozzle in 3D printing or a spinning cutter in CNC milling.
Milling refers to a reductive process of removing material with a rotating cutter that has knife edges to slice off chips. This is an old process dating back to the 1700s. Nobody knows exactly the origins. Today we use precision stepper motors to move the ‘tool’ very precisely via electrical pulses. Many CNC machines can resolve to one-thousandth of a millimeter.
CNC Workflow
The following three stages are required in order to command a CNC machine to perform an operation.
CAD - Computer-Aided Design The part must be drawn in a CAD program as vectors, surfaces, mesh or solids.
CAM - Computer Aided Manufacture These CAD drawing elements are then imported into CAM software. This takes information from the CAD file and combines it with user-defined parameters, which are subsequently converted into gcode; a sequential numerical list of toolpaths and instructions
CNC - Computer Numerically Controlled gcode is then loaded into the machine controller, the controller reads the gcode and converts this code into machine movements.
Types of CNC
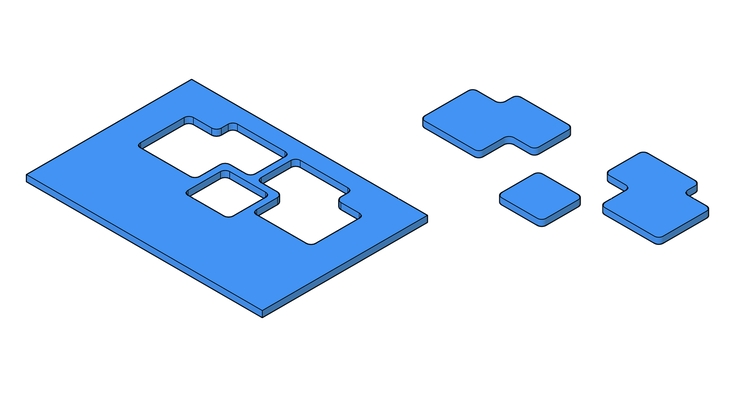
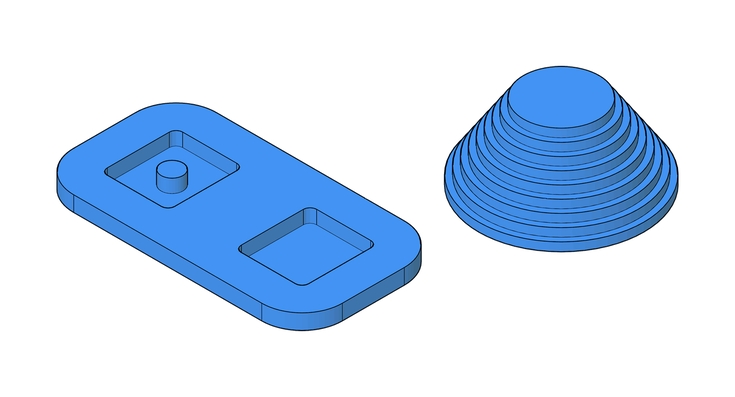
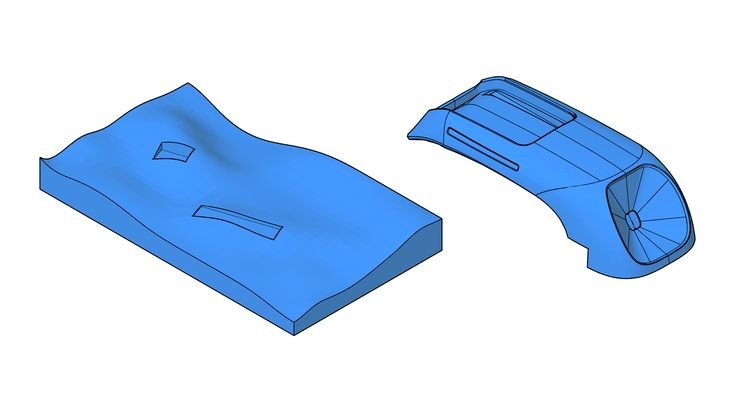
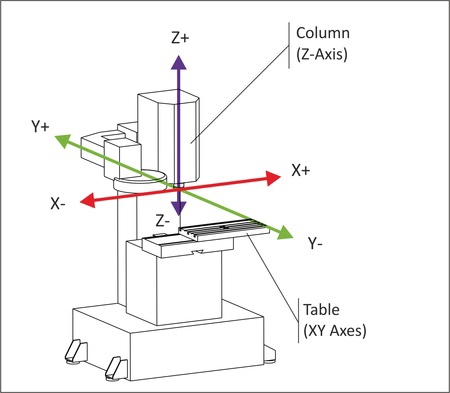
CNC milling can be classified according to the type of cuts being made. This is also related to the number of machine axis movements required to make the cuts. An axis refers to a direction of movement, so 3 axis machine will move in the familiar X,Y,Z.
How Axis Movement is Defined
Mill
Router
Lathe
Last updated